
The SCADA refers to the process of acquiring and controlling data. Supervisory control and data acquisition of industrial processes are the two core functions of the system. PLC means Programmable Logic Controller. The machine control device serves factories to automate their procedures through its integrated control mechanisms.
The misunderstanding between SCADA and PLC exists because industries use both systems for automation. But they are not the same. A SCADA system monitors as the command center of the operation whereas a PLC functions as the physical execution unit. Learning about their functions enables one to select suitable industrial systems.
SCADA systems obtain operational information through various devices including sensors along with equipment. Staff members see plant conditions through the screens that display gathered data. A PLC executes the instructions sent to manage motors and pumps alongside other equipment. The systems collaborate during operation although their responsibilities remain distinct from one another.
Introduction to SCADA and PLC
SCADA and PLC systems play an important role in industrial automation. These systems enable the monitoring and management of machines as well as industrial procedures. SCADA is a system that acquires and controls data. The system gathers information from machines which display the data on computer screens. The system displays real-time data so operators can monitor current operations.
PLC stands for Programmable Logic Controller. Machines are controlled by small computers. A set program operates to activate or deactivate machines. PLCs are fast and reliable. The combination of SCADA and PLC creates an operational system which enhances industrial safety and operational ease.
Working Principle of PLC
The Programmable Logic Controller reads signals from sensors and switches as its initial function. The system verifies incoming inputs then executes the instructions written in its program. The program determines next actions. Signals from the PLC are used to control motors, valves, and lights.
Most PLC programs are developed through ladder logic code. Each instruction is swiftly checked through sequential steps in the program. The PLC executes this series of cycles numerous times within one second. The machines operate properly while maintaining quick responses to changing conditions because of this process.
How SCADA Systems Function?
The data collection process of SCADA systems involves information retrieval from various machines alongside sensors. The system distributes this information to an operating center computer. The central computer displays data through screens to allow operators real-time observation of systems. SCADA systems detect problems which trigger warning alerts to users.
Through SCADA operators can execute remote control of their machines. Through the system operators possess the ability to power up or shut down various devices. The system stores data which becomes available for later review. The process enhancement and defect identification are possible through this system. The system enhances both speed of operation and control monitoring capabilities.
Key Components of SCADA and PLC
The core components of SCADA include sensors together with RTUs or PLCs and a central computer and user interface. The sensors utilized by the system gather information about temperature and pressure. The SCADA computer receives data from RTUs (Remote Terminal Units) or PLCs. All system data is stored within the central computer and displayed through it. Through its user interface operators both monitor the system status and execute control actions.
The main components of PLC include three elements which are the input module together with CPU and finally the output module. The input module functions by reading signals that originate from sensors and switches. The PLC operates through its CPU which acts as its central processing unit. The program execution enables decision making. Through the output module controllers receive instructions that activate motors as well as lights. The system components unite to operate equipment efficiently.
Comparison of Features and Capabilities
SCADA operates with unique features that differ from the characteristics of PLC. A primary function of SCADA is enabling remote observation and system management from a central location. The system possesses capabilities to gather data from multiple machinery devices which it then stores and displays. The SCADA system functions best in environments spanning extensive locations such as water facilities or electrical power generators and industrial complexes. Users can identify system issues promptly with SCADA systems which enables them to respond immediately.
PLCs operate to manage machines without intermediary functions. Their speed operation stands alongside their exceptional dependability level. PLCs find their applications in scenarios that require rapid control actions such as motor and light management. The main distinctions appear in this basic table.
| Feature | SCADA | PLC |
| Main Use | Monitoring and control | Machine control |
| Data Storage | Yes | No |
| Speed | Slower | Very fast |
| User Interface | Graphical (screens, charts) | No user interface |
| Control Area | Large (many devices) | Small (one machine or area) |
Applications in Industrial Automation
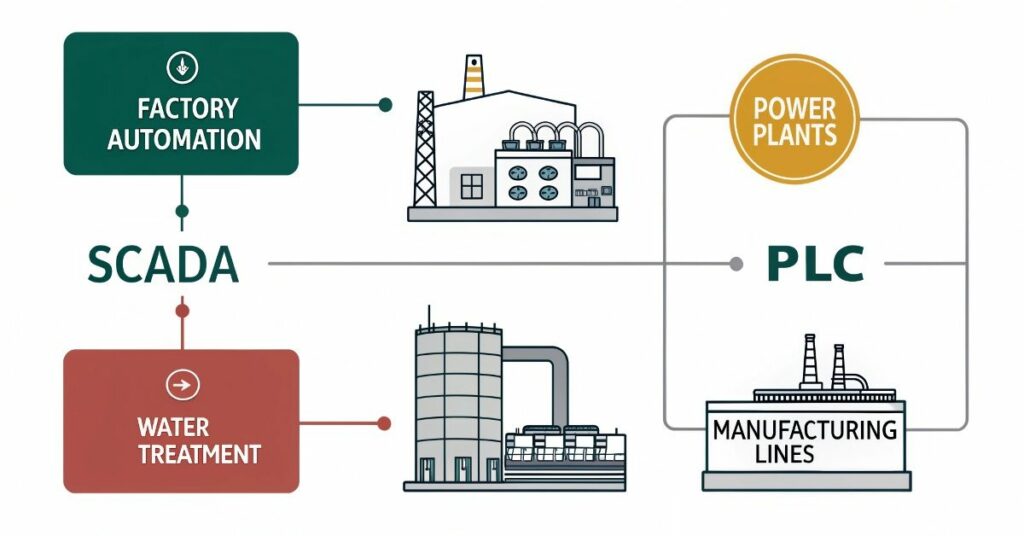
Production facilities commonly employ both SCADA and PLC for their automation purposes. Industrial automation technology enables speed-up of productions while maintaining operational safety and efficiency. The main purpose of SCADA systems involves both remote system monitoring and centralized operation control. Manufacturers employ PLC technology to manage factory-floor devices and their manufacturing sequences.
Here are some common applications:
SCADA:
- Power plants and electricity grids
- Water treatment and supply systems
- Oil and gas pipelines
- Building management systems
PLC:
- Conveyor belts in factories
- Automatic doors and elevators
- Packaging and labeling machines
- Traffic light control systems
Final Differences and Conclusion
The automation functions of SCADA and PLC are different from each other. SCADA operates as a system which carries out central management and surveillance of various systems. Through real-time data display it helps users to operate multiple devices simultaneously. The system uses PLC to execute machine operation. The system operates at a fast speed to execute commands regarding device activation and deactivation.
The automation world depends on the essential role of SCADA together with PLC. SCADA serves as the optimal solution for studying and controlling extensive systems. PLC provides the fastest control capabilities for operating machines. Industries achieve smooth production efficiency through the collaboration of these two systems. Knowledge about their distinguishing features enables suitable selection between these systems for different tasks.
FAQ’s
SCADA vs. PLC: what are the main differences?
SCADA operates to monitor and control extensive systems but PLC runs machines individually.
Can SCADA and PLC work together?
The collaboration between SCADA and PLC occurs when SCADA monitoring operates through sending control commands that PLC implements.
Where are SCADA and PLC commonly used?
SCADA systems control power plant facilities but PLC technology operates conveyor machines as well as packaging equipment.
Conclusion
An industrial automation system consists of two essential components: SCADA and PLC. Users can operate and observe large systems through a single centralized monitoring facility with the aid of SCADA. Those systems exhibit data through screens and provide operators with remote control functions. PLC operates machines with speed while performing direct control functions. This system operates at a quick pace for executing precise applied actions.
Each system displays unique advantages in its operations. Both SCADA networks function well with large systems yet PLCs work best at machine control level. Used in combination these programs help industrial work run more efficiently and securely. Knowledge of a system’s function enables suitable selection of the proper system for specific tasks.

