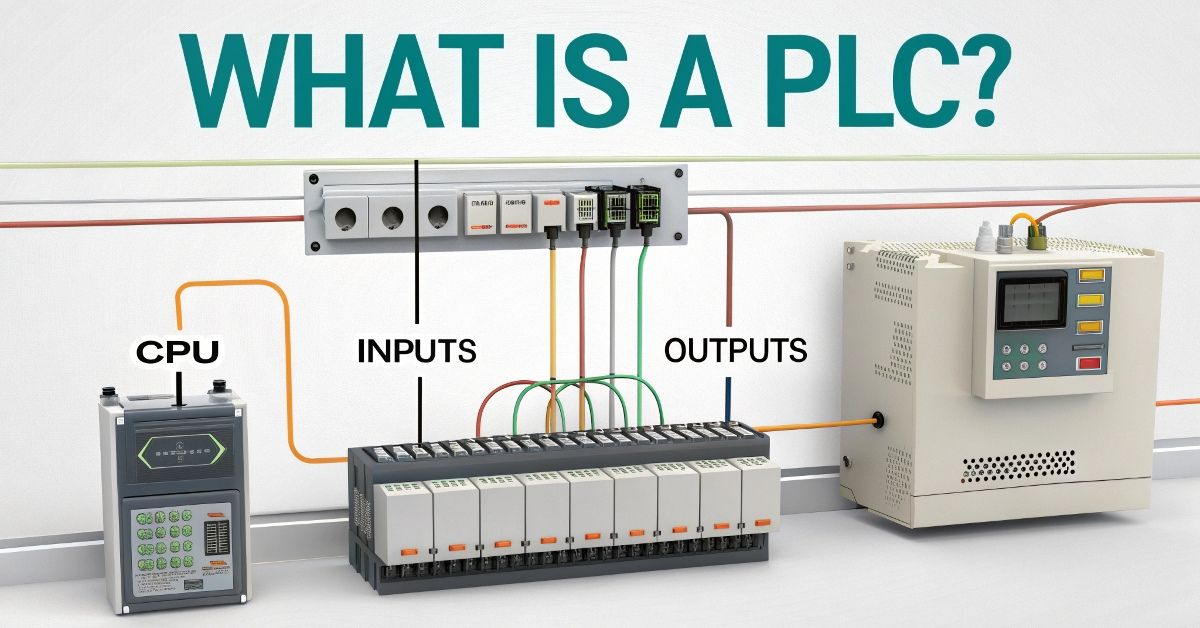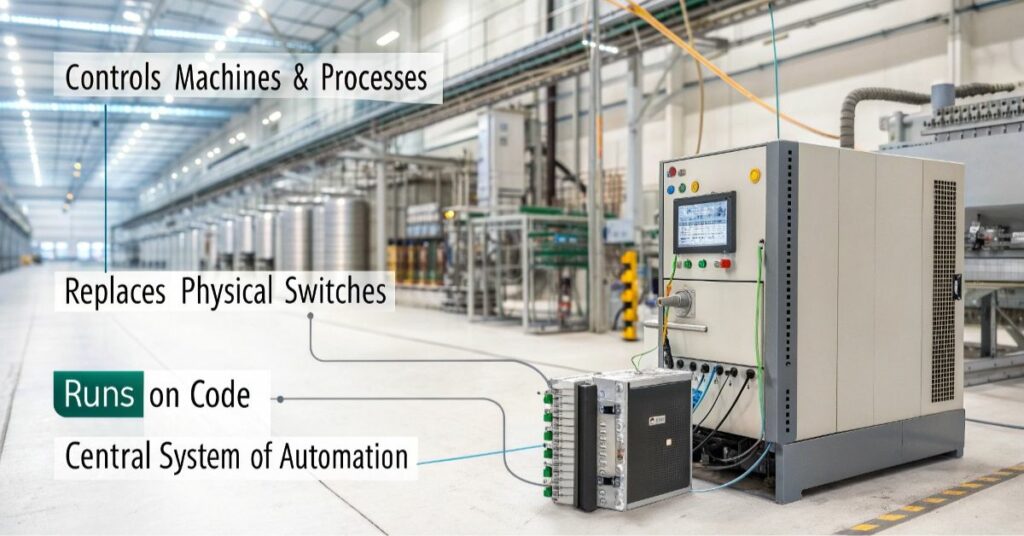
The Programmable Logic Controller which stands for PLC operates as a small industrial computer. The controller regulates machines and processes together with controlling the operations of industrial factories. The device operates using code instead of physical switches and buttons. The automated systems depend on to function as their central operating system.
The operation of traffic lights as well as fast soda bottling processes in plants remains a mystery to many people. Stand as unappreciated but essential components that power the modern industrial sector. These machines operate in the shadows but maintain every system running when left unappreciated. The information in this paper will be interesting to anyone who shows the slightest curiosity about operating processes.
Understanding the Basics of a PLC
A PLC operates as a computerized switchboard system which receives information from sensors and delivers instructions to devices. Sensors are enabled to receive information before machines follow their programmed instructions. The button operation leads to an immediate reaction from the system. Simple as that. The system runs instructions which resemble text-based programming code similar to a written recipe.
Real-time operations include counting devices while performing measurement functions together with switching applications. The system requires a package sorting system based on weight measurements. Yep, that too. They’re small but mighty. Observing everything PLCs can perform will leave anyone astonished with their capabilities.
Key Components of a PLC System
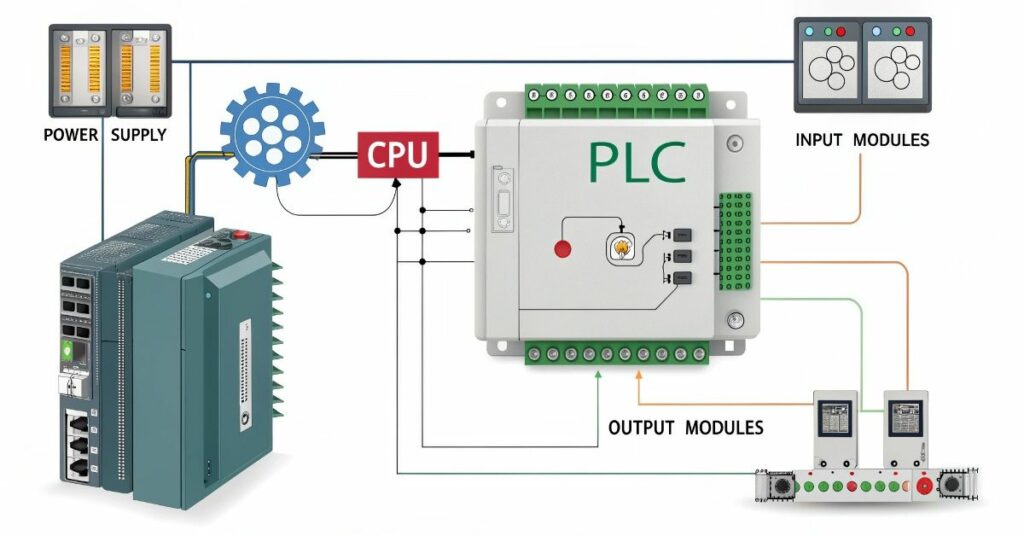
Multiple essential components within a PLC system coordinate their activities just like the mechanism of a clock. The CPU acts as the decision-making authority which functions according to the code supplied to it. Thanks to its power supply the system carries out every necessary function. The input signals through sensors through the input modules followed by the output modules directing commands to control devices such as motors or lights.
The actual most exciting interaction occurs between the components of these machine components. The program logic is distributed among different modules which maintain an active involvement for reading inputs and running operations and controlling signals. They require communication interfaces to link up with external systems through a system that works much like machine walkie-talkies. The execution of automation relies on the unified work of each component between the power supply and input and output modules.
How PLCs Work? The Operating Cycle
This never-ending loop is known as the scan cycle which operates in a tight continuous manner. A PLC starts its operation by understanding all input commands that come from switches, sensors and buttons. As a second step the program gets examined for required actions. The system finishes by updating the output components which might include operating motors or turning lights on or activating valves. All stages of this process complete execution in a brief period under one millisecond.
PLCs achieve their dependability through their live operational process. A rapid response capability to changes happens immediately since this matter of timing. Your conveyer belt will continue moving a single second beyond its intended stop time before products flare into disarray. During the scan cycle all operations execute without issues as programmed. Using this system produces the focused performance of an employee who stays sharp without any coffee stops or breaks.
Programming a PLC: Languages and Logic
All PLCs operate through several standardized programming languages. The most popular programming language is Ladder Logic because its electrical diagram format enables electricians to learn it easily. Function Block Diagram operates through sections similar to puzzle shapes connecting with one another. Utilize Structured Text as a programming language that functions similarly to writing operational instructions in regular English text. Programmable Logic Controllers operate using various programming languages which different groups of people find preferable between them. The choice often depends on your project needs together with your mental processing method.
The PLC operates based on programmed instructions that depend on incoming data. The machines execute basic logic commands to achieve precise control functions. Through your established guidelines the PLC operates accordingly:
- Check if a sensor is on or off
- Decide what action to take
- Turn devices on or off
- Repeat the process every few milliseconds
Real-World Applications of PLCs
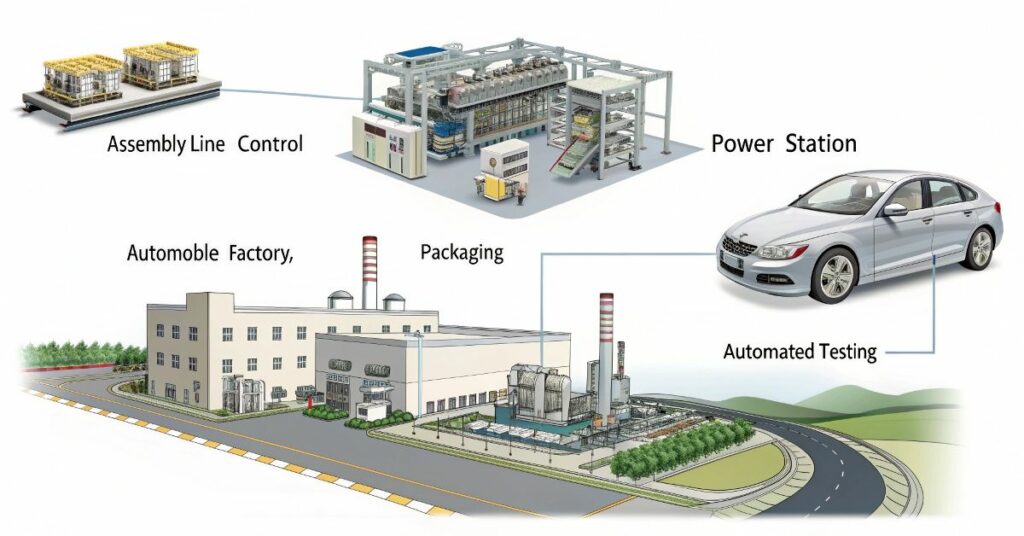
You can find PLC systems working throughout all industries while directing operations unnoticed. Production facilities as well as automobile factories and food manufacturing lines and power stations utilize these devices. Transitioning from home to work seems obsolete when laboring invisible professionals continuously operate at their posts without stopping. Systems control operations in all automated systems that require both precise timing and movement sequences. Every business sector depends on some level for operation.
Operate as programmed controllers that handle unappealing aspects of product sorting along with vehicle frame welding. Perform their tasks without becoming bored or tired or experiencing any form of distraction.
| Task | Description |
| Assembly Line Control | Keeps machines moving in the right order |
| Packaging | Boxes, seals, and labels products fast |
| Automated Testing | Checks parts or products without human help |
Benefits of Using PLCs in Automation
The programming logic controller provides sturdy capabilities combined with programmable adaptability and straightforward maintenance capabilities in abnormal situations. The modern control systems prove superior to old-fashioned systems due to their dependable nature. The ability to easily upgrade operations stands as their most significant achievement according to my assessment. A few short lines of programming code can enable new module connection through simple plugging and you will be ready to operate. Repairing PLC systems is straightforward because you only need to edit program code before fixing any issues without dismantling everything.
The Future of PLCs in Industry
Manufacturing intelligence expansion causes these small control devices to learn sophisticated capabilities. They connect with cloud systems while exchanging information with other machines in addition to processing higher volumes of data than they used to. These little control stations combine better processors with smarter software to function as the central processing units of high-speed and high-precision operations. PlCs will greatly contribute to make automation more efficient and waste-free in industrial operations. Every business actively uses products that enhance manufacturing output with no financial strain as these innovations prove to be enduring.
FAQ’s
What does a PLC do?
The real-time operation of a happens through its capability to read input signals followed by logical program execution and output signal control. The automated system possesses its brain within the PLC.
From a typical computer what key distinctions exist in PLC functionality?
Unlike regular computers, PLCs are built for industrial environments. They withstand extreme conditions, run 24/7, and execute tasks with precise timing.
Is it possible to modify the programming of PLCs for different operational purposes?
Yes! PLCs are highly flexible. The programming can be updated to support new processes thus providing cost-effective long-term application potential.
Conclusion
Modern automation operates through the unflattering yet indispensable operation of PLCs. The primary role of a Programmable Logic Controller consists of operating industrial machines and factory operations. Multiple industries choose because they deliver reliable systems along with flexible operation and real-time control. Enable smooth operations throughout manufacturing facilities as well as automotive plants and food processing facilities.
Irrespective of current trends s will continuously improve their capabilities. The advancements in technology will enable us to establish numerous system connections while becoming more proficient at carrying out substantial responsibilities. According to my view the plastic logic controller will remain the essential infrastructure which maintains efficiency and competitive power in industrial operations.