Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition systems known as SCADA serve enterprises for industrial process monitoring and control needs. The system enables the collection of current data which originates from different sensor and device inputs. The centralized system of control through SCADA makes it possible to handle intricate operations more efficiently.
Operating a factory that requires you to supervise its machines as well as equipment while continuously managing every process. Through SCADA automation you can monitor every operation with ease from one central point which results in continued system efficiency and accelerated responses to system troubles. Multiple industries use it as their fundamental operational structure which extends throughout manufacturing and utilities.
SCADA automation gives businesses enhanced operational security along with higher efficiency and less production interruptions. The system enhances business decision quality through its data delivery while eliminating the requirement for human-operated control.
Introduction to SCADA Automation
The industrial operations receive management and surveillance functions through SCADA automation systems. Through different sensors and devices the system obtains data which operator’s access from a single unified location. The system finds applications throughout manufacturing operations as well as utility sectors and water facilities.
Real-time process tracking occurs through SCADA automation systems in businesses. Such a system helps businesses identify problems early in order to minimize equipment downtime alongside enhancing operational efficiency. Automation through SCADA enables safe operations that need minimum human oversight by performing various tasks.
Key Components of SCADA Systems

The SCADA framework consists of essential components which collaborate to monitor together with control operational processes. An SCADA system consists of four essential parts that are sensors and controllers with built-in communication systems and user interfaces. The system depends on each component to function properly while it collects data, forwards it to a central location and shows it to operators.
Quick and main components of SCADA systems:
| Component | Description |
| Sensors | Obtain data from both machines and production processes. |
| Controllers | Decision-making relies on processed data from system inputs. |
| Communication System | Transmits data between sensors, controllers, and central systems. |
| Human-Machine Interface (HMI) | This system presents data which operators need to monitor process control activities. |
How SCADA Automation Works?

The central system of SCADA automation will link all sensor controllers and other devices together. Real-time machine process readings are recorded by sensors that measure things such as temperature and pressure along with flow rate. The data gets transmitted to controllers and these components execute their processing and adjustment procedures based on the received information.
After reaching the central system the information gets displayed through the Human-Machine Interface (HMI). Malfunctions quickly become detectable by operators through their monitoring screen which enables them to perform needed tasks. Through SCADA automation it becomes possible to operate processes from a distance which decreases the necessity for on-site personnel while monitoring.
Benefits of SCADA Automation in Industries
Through SCADA automation businesses gain two main benefits which combine operational efficiency with security safety. The facility to monitor processes and control them instantly helps both early issue detection and prevents system downtime costs. System operators enhance productivity by speeding up problem response which decreases the requirement for human intervention.
Key benefits of SCADA automation:
- Improved Efficiency: Automated processes run smoothly with minimal human error.
- Cost Savings: Initial issue detection leads to reduced equipment operational disruptions as well as lower maintenance costs.
- Enhanced Safety: SCADA helps identify unsafe conditions, preventing accidents.
- Remote Monitoring: System management becomes simpler because operators can command their systems from any location.
- Better Data Collection: The method generates important information that supports optimization decisions.
Types of SCADA Systems
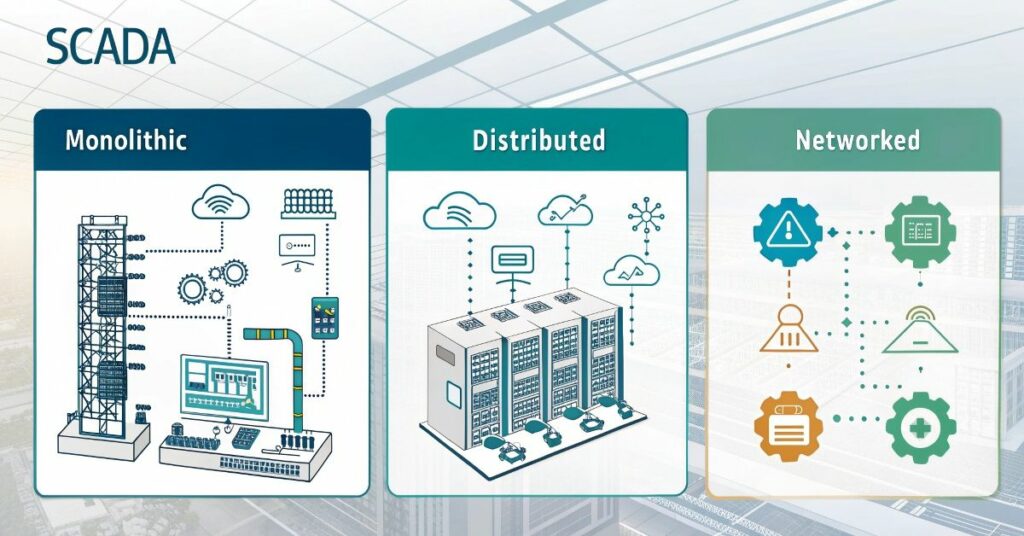
SCADA systems exist in specific types that match industry requirements. There are two fundamental SCADA system varieties including monolithic systems and distributed systems. All control operations alongside data collection processes for monolithic systems occur at a single central location. Systems with centralized control remain simple to operate yet present limitations for big-scale industrial operations.
A distributed SCADA system distributes its controllers across several sites. These systems enable better flexibility together with scalability particularly for businesses operating with extensive complexity. Distributed systems enhance operation speed and respond swiftly because they process data at locations near its original sources. The two types of SCADA systems operate at opposite ends of monitoring while achieving control objectives for industrial operations.
Applications of SCADA Automation in Different Sectors
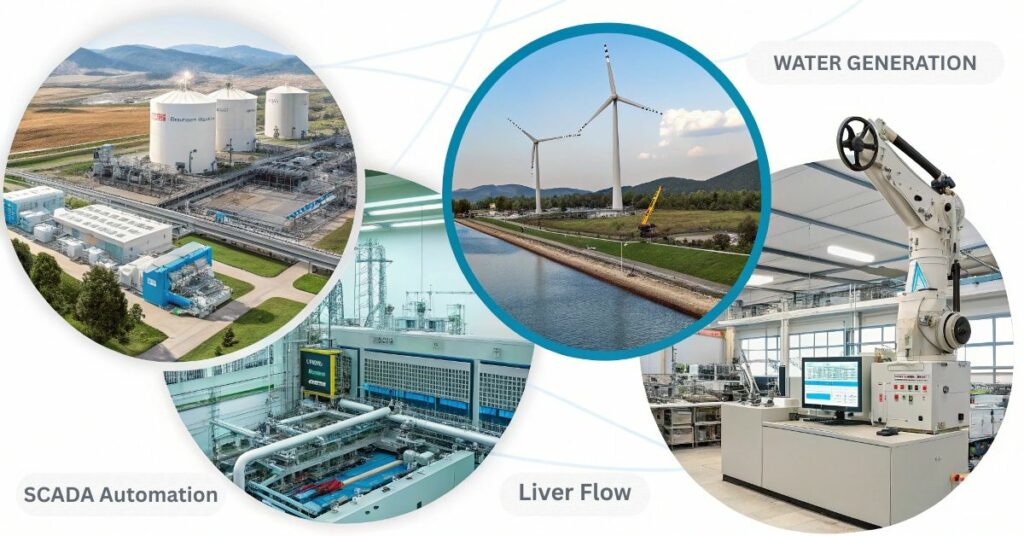
Various industries implement SCADA automation for more efficient automation and control capabilities. The energy sector utilizes SCADA systems for electrical grids management as well as renewable energy source operation and power plant supervision. Electricity supply remains stable through automatic system adjustments and fault detection capabilities of these devices. The monitoring of water quality and flow rates along with the management of tank levels by SCADA allows safe distribution of treated water from treatment plants.
The manufacturing industry utilizes these systems as they watch production lines and examine equipment behavior to generate operational efficiency improvement throughout manufacturing processes. The control of oil pipelines along with drilling rigs and refineries through SCADA automation enables safe resource management in the industry. The SCADA system serves various industries like transportation and agriculture together with building management since it increases productivity and minimizes errors.
Future Trends in SCADA Automation
SCADA automation faces quick evolutionary changes because of technological progress together with industrial demands for better automation efficiency and enhanced security alongside scalability. The connection to Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) enables SCADA systems to retrieve real-time information from extensive connected devices which improves both decisions and equipment maintenance forecasting abilities.
Artificial intelligence (AI) alongside machine learning (ML) technologies have started to reengineer SCADA systems by giving them the capability to process extensive data amounts for detecting irregularities and enhancing operation procedures while anticipating maintenance needs. Fully developed Human-Machine Interfaces with virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) technologies help users achieve better industrial process control by delivering natural and immersive operational experience.
FAQ’s
What is SCADA Automation?
SCADA automation functions as a system which gathers real-time sensor data from industrial equipment to both monitor and control operations throughout industrial facilities.
What are the principal advantages of implementing SCADA automation systems?
The implementation of SCADA automation creates efficient operations while reducing equipment failures and enhances safety measures which enables remote monitoring activities that generate financial benefits and improved decision quality.
What changes will take place in SCADA automation to advance its future capabilities?
The advancement of SCADA infrastructure incorporates IIoT and AI and cloud technology to achieve quicker and more efficient while more secure industrial control.
Conclusion
The ability of SCADA automation to monitor and control operations in real-time serves as a vital factor which enhances industrial performance. The system improves operational efficiency together with safety conditions and enhances decision capabilities through decreased downtime and reduced expenses. Delivery of complex procedures through SCADA systems enables industrial operations to function safely as well as continuously.
The future of SCADA automation appears promising because technology continues to advance. The combination of cloud platforms and AI as well as IIoT technology enables systems to become more powerful alongside becoming more flexible. The future development of SCADA automation technologies will improve industrial operational monitoring capabilities thus establishing this system as an essential operational tool.

