
SCADA stands for supervisory control and data acquisition. SCADA establishes itself as a monitoring system which controls industrial process functions through its operations. HMI means Human-Machine Interface. The human-machine interface operates as a connection bridge which presents data between people operating machines through its display elements.
Individuals often wonder about how factory operators and power plant personnel maintain control from central locations. Using SCADA and HMI, this operation is possible. Through these systems people can control and monitor large operational systems efficiently and securely. Confusion exists between these two systems among most people who encounter them.
The biggest distinction arises from SCADA being an entire system which HMI operates as a component within that system. The SCADA system retrieves data simultaneously with command distribution and process management functions. The HMI presents data through screens while providing operators with control functions for machines.
Introduction to SCADA and HMI
System management happens through SCADA and HMI processes. In both terms, supervisory control and data acquisition systems are described as SCADA. The system acquires machine data that gets transferred to the computer. Remote operators utilize acquisition data to build decisions which lead to system control through operational methods.
HMI stands for Human-Machine Interface. A display shows system proceedings to users through its screen function. Workers access machines utilizing buttons as well as graphics and touch screen interfaces which incorporate Human-Machine Interfaces. Industrial safety and operational convenience result from the combination of SCADA and HMI systems.
Basic Functionality Comparison
SCADA and HMI have different roles but work closely together. SCADA is a full system that manages and controls large processes. The system receives sensor information and device data before using it to issue commands. HMI is the part that shows the data to the operator and lets them give inputs.
Here are some basic functions:
SCADA:
- Collects real-time data
- Sends alerts and alarms
- Controls devices remotely
- Stores data for future use
HMI:
- Displays system data
- Shows alarms and messages
- Let’s users control machines
- The interface includes buttons as well as menus and visuals that make the system easy to operate.
System Architecture and Components
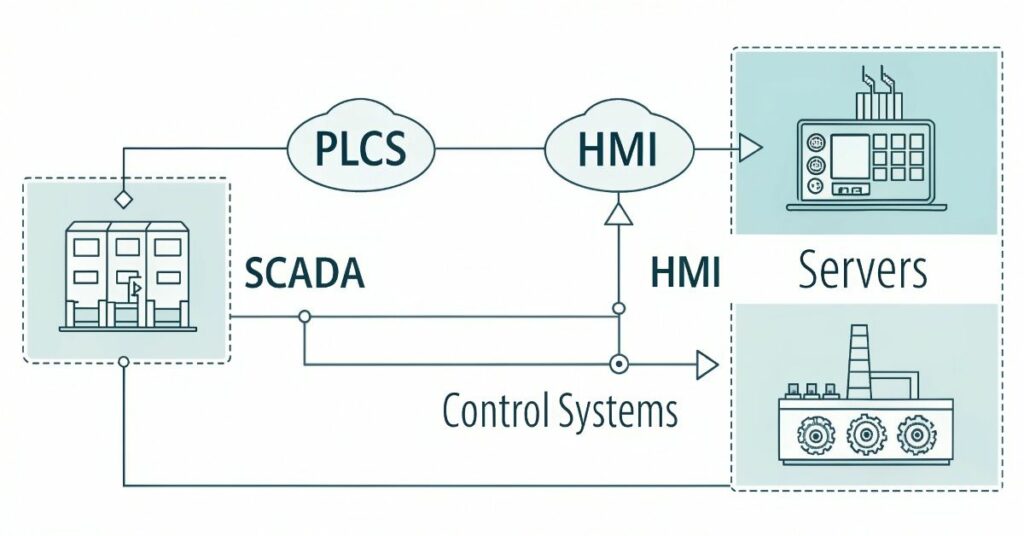
SCADA has a complex system structure. An SCADA system consists of sensors together with remote terminal units (RTUs) and programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and communication networks that connect to a central computer. The sensors collect data from machines. Data from PLCs and RTUs are sent to a central computer. Data is processed and control commands are sent by the computer.
HMI is a part of the SCADA system. It is usually a screen or panel connected to the PLC or central computer. The representation of data appears through visual elements combined with textual information. Operators use it to check machine status and control operations. People are able to understand and manage the system more easily thanks to the HMI.
User Interface and Control Features

HMI has a user-friendly interface. The interface displays current data through visualization combinations of charts, buttons and images. Machine control is possible through screen touch inputs or mouse operations. Users can quickly understand the ongoing situation as well as perform needed actions through the interface.
SCADA also has control features but works on a bigger level. It connects many HMIs and systems together. Through this system operators maintain control of multiple machines from a single operational center. SCADA provides users with warning notifications and documentation which enables better decision-making.
Data Handling and Communication
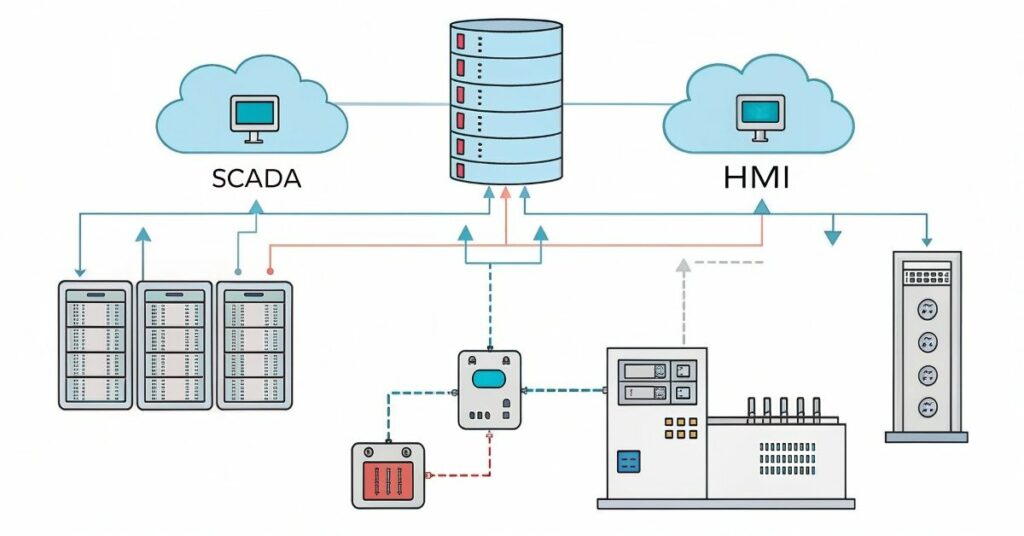
SCADA handles a large amount of data. The system retrieves current machine data which gets saved into a database. The solution tracks ongoing data collection from machines while it stores information in a database and generates warning notifications for any detected issues. SCADA uses communication networks to send and receive data from different parts of the system.
The HMI also deals with data, but in a much smaller way. Users can view screen data because HMI shows it for their observation. It gets data from the PLC or SCADA system. Using the HMI, the machines receive user commands. Controlling the process in this way is simple and clear.
Applications in Industrial Automation

Various industrial sectors implement it including power generation stations, water treatment plants and operations within the oil and gas sector and manufacturing facilities. By means of central monitoring SCADA enables operations management to run more efficiently and achieve enhanced safety measures. Industrial safety and operational convenience result from the combination of SCADA and HMI systems.
Human-machine interfaces (HMIs) are used everywhere machines need to be interacted with. The system is present in manufacturing environments as well as packaging facilities and building management systems. With HMI workers obtain simple methods to operate machines while swiftly addressing operational issues. SCADA and HMI operate as a united system to enhance industrial automation efficiency.
Key Differences and Final Comparison
The SCADA system operates under a partnership with HMI where each component handles its individual tasks. The SCADA system functions as a data acquisition platform that operates machine control and manages operational processes. The primary purpose of HMIs is to show data and accept user input through their display screens. The wide geographical coverage belongs to SCADA systems but HMI functions at the operator’s local workstation.
Basic table SCADA and HMI:
| Feature | SCADA | HMI |
| Full System | Yes | No (part of SCADA) |
| Main Role | Data collection & control | User interaction |
| Data Storage | Yes | No |
| Control Area | Large/Multiple locations | Local/Machine level |
| User Interface | Basic to advanced | Touchscreen/Graphical display |
FAQ’s
SCADA and HMI: what are the main differences?
The SCADA control system operates as a complete process management system which enables users to interact with machines through an HMI interface.
Can SCADA work without HMI?
The system operates but HMI provides the crucial graphical interface for user interactions with the SCADA system.
SCADA and HMI software applications find their primary applications in which specific areas?
The industry sector applies these devices across power plants and water treatment facilities and manufacturing sites and oil and gas facilities to manage operations.
Conclusion
SCADA and HMI are important parts of industrial automation. The control and monitoring functions of SCADA systems operate with HMI interfaces that provide user interactions for these systems. Operations function smoothly and efficiently alongside safety issues through the collaborative effort of these systems.
Identifying the distinctions enables users to select appropriate systems that match their requirements. The main responsibility of SCADA includes managing overall operations while HMI enables user interface control. Both play a key role in improving industrial performance and decision-making.

