The basic functioning principle of many automated techniques operates through PLCs. The core features of PLCs enable them to interface with physical devices including sensors along with motors and switches. Learning about the methods PLCs use to operate devices stands as the essential foundation for automation expertise.
The interaction operates through inputs and outputs which people also name I/Os. A system sends outside world information through its inputs to control machines through its outputs. Understand that digital, analog and specialty modules differ in purpose because each serves an individual function.
Your automation project success depends heavily on making suitable I/O module decisions. The selection depends on speed capabilities as well as environmental conditions and future growth needs. Your system performance benefits from appropriate setups to deliver more speed and reliability along with smoother operations.
What Are PLC Inputs and Outputs?
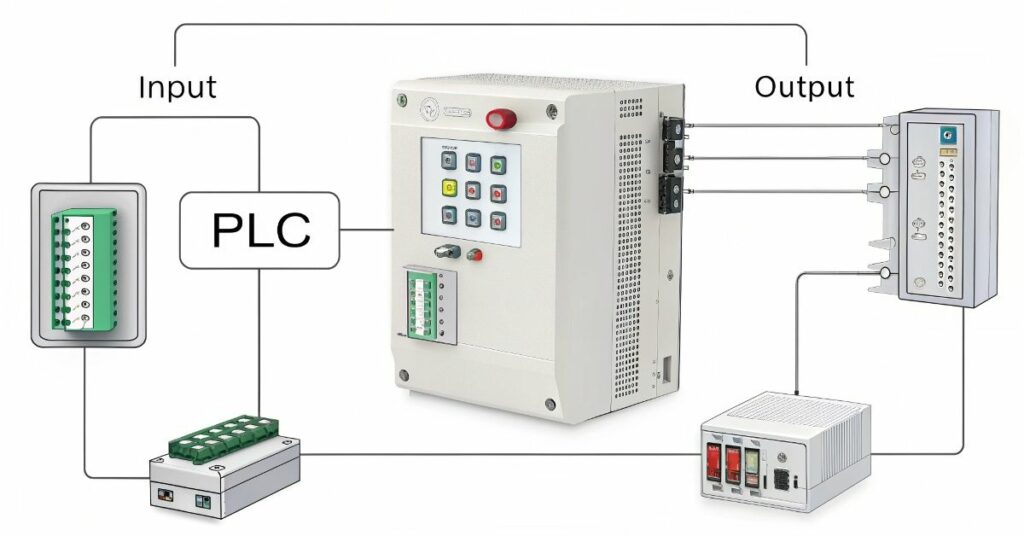
The central function in a PLC system depends on inputs together with outputs to allow interaction with external environments. Obtain their information through signals which sensors and switches transmit into the system. Premium devices receive their commands through outputs of commands sent to motors or lights to enable action triggers. The ability of automation systems to pass information dynamically enables them to achieve their tremendous power.
The central role in I/O operations belongs to I/O modules. The I/O modules function as the connection point between PLC systems and physical devices. Signals between and its physical devices are impossible without appropriate I/O modules. I believe selecting top-quality I/O modules remains essential because they determine how well an automation system functions and maintains its dependability.
How PLCs Handle Inputs and Outputs?
This sequential process of PLCs enables them to process system inputs and send corresponding outputs thus enabling automation. An input device transmits a signal that enables the PLC to process data through its programmed instructions. After processing input signals the result goes out to control an external device as an output command. The data-processing mechanism along with a stream of actions helps automated systems operate effectively.
Here’s how it works in simple terms:
- Inputs: Devices like sensors or switches send signals to the PLC.
- Processing: The reads the input and processes it according to its program.
- Outputs: Based on the processed data, the PLC sends commands to control machines or devices.
- Feedback Loop: This cycle repeats continuously, ensuring systems stay responsive and efficient.
How PLCs Process Input Signals?
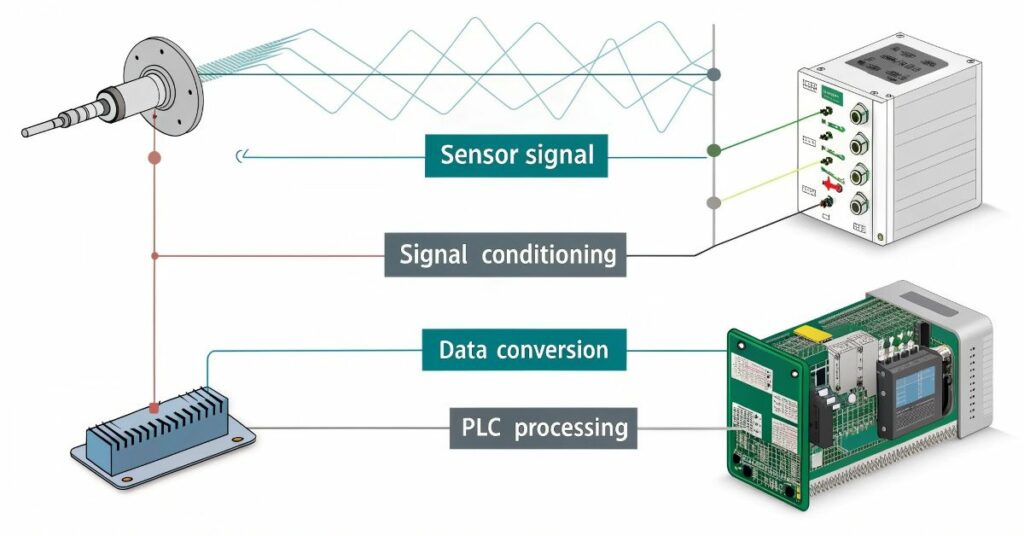
The first stage in PLC inputs entails signal conditioning before conversion into usable data. The process of signal conditioning produces clean input signals that maintain ranges suitable for processing raw data especially from sensors. Such processing step prevents mistakes and elevates input signal precision. The PLC proceeds to transform the signal into a format that it understands such as digital or analog following signal conditioning steps. The proper conditioning stands as an essential development step since incorrect data and excessive noise would result.
How PLCs Execute Output Commands?

The output commands output control signals from a PLC which follows the logic decisions contained in the program. It analyzes inputs before it uses its program to trigger appropriate executable actions such as activating motors or opening valves. I believe the decision-making approach makes it powerful and adaptable for automation systems.
Such outputs become possible at their proper time through carefully timed combinations with sequencing and appropriate feedback. Specific timing prevents errors from occurring and sequencing enforces operations to happen in the correct sequence. Feedback provided by the system helps PLCs readjust their outputs for maintaining smooth operations which leads to more reliable and efficient performance of the entire system.
Selecting the Right I/O Modules for Your Application
The selection of I/O modules for an application requires you to think about several important points. The voltage requirements need to correspond exactly with your existing devices. The I/O modules need to provide functionality for voltage operation at 24V when sensors use that power level. You should determine whether your signals function as digital or analog types. The successful operation of accurate data collection and control requires selecting the correct type of module because each version exhibits particular characteristics. The environmental factors must be taken into consideration during your selection process.
I/O modules require evaluation for their capacity to scale as well as expand in future applications. The most beneficial choice for I/O modules should be modules which accommodate growth in system requirements. The use of I/O modules which accommodate extra inputs and outputs presents a cost-effective option against future system development because they replace the need for complete system replacement. You may require added sensors together with expanded device control options after the initial purchase.
| Factor | Considerations |
| Voltage | Ensure the module matches the device voltage range |
| Signal Type | Choose between digital or analog signals based on needs |
| Environment | Select modules designed for temperature, moisture, or dust protection |
| Scalability & Expansion | Plan for future needs with expandable I/O options |
Troubleshooting Common I/O Issues in PLCs
Interestingly PLC operation requires immediate attention to solve common I/O system problems. The main issues which arise involve wiring faults combined with signal noise as well as module failure problems. The analog signals experience incorrect readings when signal noise appears while wiring faults develop from connections that become loose or suffer damage. The stoppage of component operation or the corruption of system modules leads to module failure.
The first action when addressing problems with I/O functions should include checking wiring to detect loose parts and excessive damage. To check proper signal levels you should use a multimeter. When you suspect noise is present in the circuit you should attempt cable shielding and grounding as possible solutions. After a failed module detection it is necessary to exchange it with a verified working module then perform system tests. A systematic approach consisting of simple measures helps identify the problem as well as restore operational functionality.
FAQ’s
What are inputs and outputs in a PLC?
Inputs are signals received from devices like sensors, while outputs are commands sent to devices like motors or lights.
What is the difference between digital and analog PLC modules?
Digital modules deal with on/off signals, while analog modules handle variable signals like voltage or current levels.
How can I troubleshoot I/O problems in a PLC system?
Check for wiring issues, test module functionality, and monitor signal integrity to quickly diagnose and fix I/O-related problems.
Conclusion
The mastery of automation requires a clear comprehension of PLC input signals and output signals. These systems create a connection which permits digital signals from PLCs to reach physical operational equipment. The understanding of input-output interaction enables developers to build more dependable automated systems with better efficiency.
Choosing appropriate I/O modules alongside correctly preparing the operational setup provides substantial improvements in operational effectiveness. You can develop a system that serves current requirements and adapts to future growth through proper evaluation of signal characteristics as well as voltage conditions and environmental conditions. Your system maintenance process becomes simpler along with troubleshooting efforts because you understand each connection’s role in the system.