The main operating component of innovative control systems are PLCs and microcontrollers which empower machinery with smart capabilities. They excel uniquely within their respective domains since their purposes differ even though their skill levels remain high. Anybody who has ever pondered about industrial and home-based invention preferences.
A casual examination might cause people to confuse PLCs with microcontrollers. The majority of people become confused at this basic understanding. These integrated systems stay entirely different from one another despite their similar purposes. Industrial programmers receive their strength from being constructed like sturdy machines designed for executing challenging operations. Microcontrollers present a sleek and fast design which allows users to execute custom-made operations quickly.
Selecting between PLCs and microcontrollers involves much more than random chance selection. The selection of ideal equipment depends on what task needs to be accomplished. A production line should run using experience but a homemade gadget needs a compact microcontroller system.
Introduction to PLCs and Microcontrollers
A Programmable Logic Controller represents a rugged computer designed for factory machine control operations. Predicted tasks beyond its programmed scope do not cause the machine to pause its operation. The microcontroller functions as miniature hardware computer devices which excel at running small gadgets alongside one-off project development. The comparison between these two devices holds great importance because their applications stand entirely apart from one another. Using a bulldozer instead of flowers to plant could result from error in this situation.
Core Architecture and Components
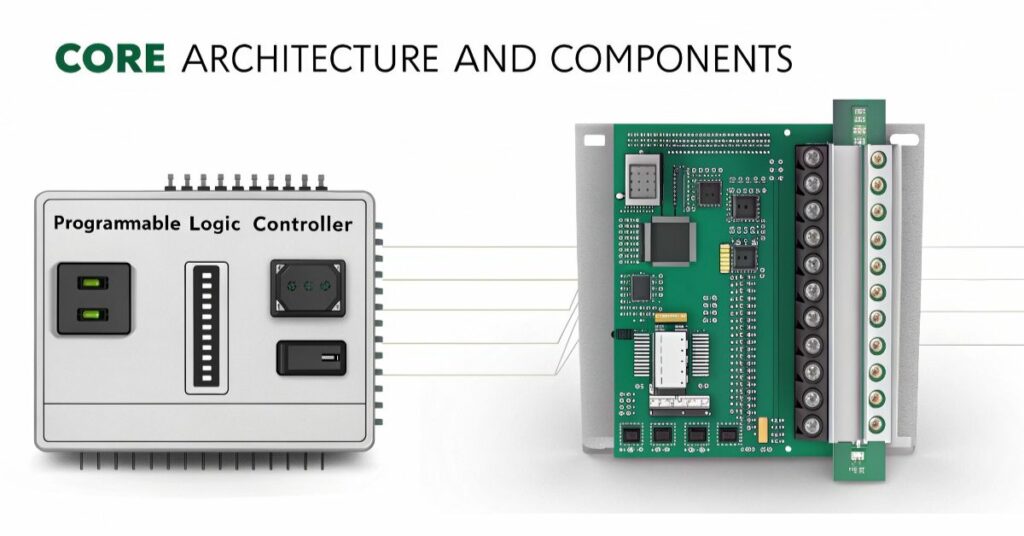
PLCs have a construction that matches brick houses. A contains all necessary components including power supply together with processor and input/output modules and specific communication ports. A durable fitted enclosure keeps all the components protected against harsh conditions from heat and noise and tough environments. The compact design of microcontrollers makes them appear neat and slim. A single microchip contains all of its processors together with memory components and input/output mechanisms.
Construction of PLCs meets requirements to tolerate harsh usage and operate controlling heavy equipment under any condition. I consider it. Microcontrollers excel as smart devices and hobbies but also serve as quick decision-making components for minor electronic systems. Thanks to their lightweight design such devices maintain quick speed performance.
Programming and User Interface
Ladder logic represents the main programming language which PLCs use for simple visual coding. The interface displays electrical diagram elements that engineers and electricians understand easily. Function block diagrams together with structured text are part of the programming capability found in certain when handling complex tasks. Traditional coding becomes the central focus of microcontrollers even though they process tasks at a deeper level. Programming requires C, C++ and assembly language which these devices use as their primary codes.
Different approaches exist in terms of user-friendliness between these two systems. The process of programming PLC devices appears more accessible to novices especially when developers approach tasks through visual logic. The process of writing code for microcontrollers requires more mental effort compared to other methods. Here’s a quick breakdown:
PLCs:
- Easier for beginners with engineering backgrounds
- Visual and logical setup (great for quick fixes)
- Limited flexibility for complex customizations
Microcontrollers:
- Steeper learning curve for non-programmers
- Full freedom to build whatever you dream up
- Powerful but needs detailed attention to small things
Industrial vs. Consumer Applications

Industrial automation benefits from PLCs as the top choice for a specific reason. Production sites rely upon these systems because they remain strong yet dependable across daily operations. A factory’s production demands lead to selection since frequent machine malfunctions would compromise their operations. PLCs require minimal maintenance while enduring intense heat together with cold temperatures and mechanical vibrations without any problems.
Microcontrollers establish their unique value in small technological products that operate enhanced capabilities. These devices operate silently in the background when used in microwave appliances as well as smart watches. Microcontrollers stand as people’s preferred devices mainly because they occupy small areas and implement programming instructions for various tasks.
Here are the features of both:
| PLCs | Microcontrollers |
| Heavy-duty factory automation | Smart home devices and wearables |
| Built for extreme environments | Built for flexibility and low power |
| Limited to structured tasks | Great for creative custom projects |
Reliability, Durability, and Environmental Resistance
The construction of PLCs resembles tanks that function under severe conditions including high temperature and wetness and powerful vibrations. These programmable controllers show indifference to factory noise as well as freezing warehouse and boiling-hot assembly line conditions. The industry puts their trust in these systems because of their ability to operate various million-dollar machines. Different approaches define microcontrollers since they differ from PLCs in fundamental ways. These electronic devices perform well in controlled living room environments as well as laptops but they become prone to cracking when exposed to harsh conditions. Severe temperature changes along with hard hits and electric disturbances will cause microcontrollers to malfunction.
Cost Considerations and Project Scale
The high price of PLCs aligns well with their mission of delivering long-term heavy-duty functionality. Large factories along with extensive systems experience excellent returns from their investment in systems. Small initiatives and cost-efficient designs benefit from microcontroller technology because they provide affordable alternatives to their counterparts. The devices are able to produce smart robust products for a cost-effective investment. Expansion of PLC systems through additional modules and support solutions becomes simpler in comparison to other systems. A project that outstrips the capability of its tiny microcontroller chip will experience limitations due to its flexible nature. The wise selection benefits users by minimizing their financial burdens and eliminating probable hassles ahead.
How to Choose: PLC or Microcontroller?
The selection between a Programmable Logic Controller or a microcontroller creates difficulty for users. Industrial factories require dependable device control through the implementation of PLCs because of their strong mechanical features. The industrial programming logic controller consists of elements suitable for manufacturing environments which easily accept programming instructions. Equipment within PLCs and microcontrollers shows resistance to high temperatures in addition to vibrating within dust-filled environments.
Small tasks require microcontrollers because they combine low cost with affordable pricing. The devices measure less than one inch yet remain reasonably affordable though they demand higher programming expertise. The development process requires coding character generation as well as circuit design alongside thorough testing protocols. Illuminating products possess increased flexibility because of microcontrollers. These devices find their best application in creating DIY electronics devices as well as robots and smart home systems.
FAQ’s
What is the main difference between a PLC and a microcontroller?
The design purpose of a PLC ensures high durability for industrial applications while microcontrollers focus on embedded control in consumer and electronic devices.
Programming a PLC presents more difficulty compared to microcontroller programming?
PLCs are considered simpler for initial programming learners as they use ladder logic visual programming format while microcontrollers need beginner programmers to write code in C or C++ programming languages.
What scenario justifies employing a PLC instead of selecting a microcontroller?
Choose a PLC because of its exceptional reliability as well as its convenient maintenance features and tolerance to harsh industrial conditions.
Conclusion
Your project requirements determine whether you should choose between using either a PLC or a microcontroller. The best solution for factories demanding strong usable equipment is a PLC. The device operates in demanding environments and users can program it easily. A person without advanced coding proficiency can utilize this system successfully.
The selection of a microcontroller makes more sense when developing small low-cost personal or budget-driven projects. You obtain more control and freedom from this device yet you need excellent coding and circuit capabilities to benefit from it. Proper planning of your needs requires serious consideration prior to making your selection. The correct selection will improve both the performance and ease of use for your project.