Redundancy in PLC systems is the key to reliability in modern industrial environments. With machines running all the time, even a small fault can cause major problems. And that is why having a backup system ready to take over is not only smart, but also mandatory.
From my perspective, the best strategy to minimize downtime, and prevent failures, is to incorporate redundancy into your PLC architecture. Nobody enjoys working with timeout situations. When correctly configured, operation continues smoothly even if a part fails.
Redundancy not only stops problems, but it also increases the overall efficiency of automation systems. It enables factories to work more modern, effective, and confident. In the end, smooth processes provide higher productivity and stronger results.
Understanding Redundancy in PLC Systems
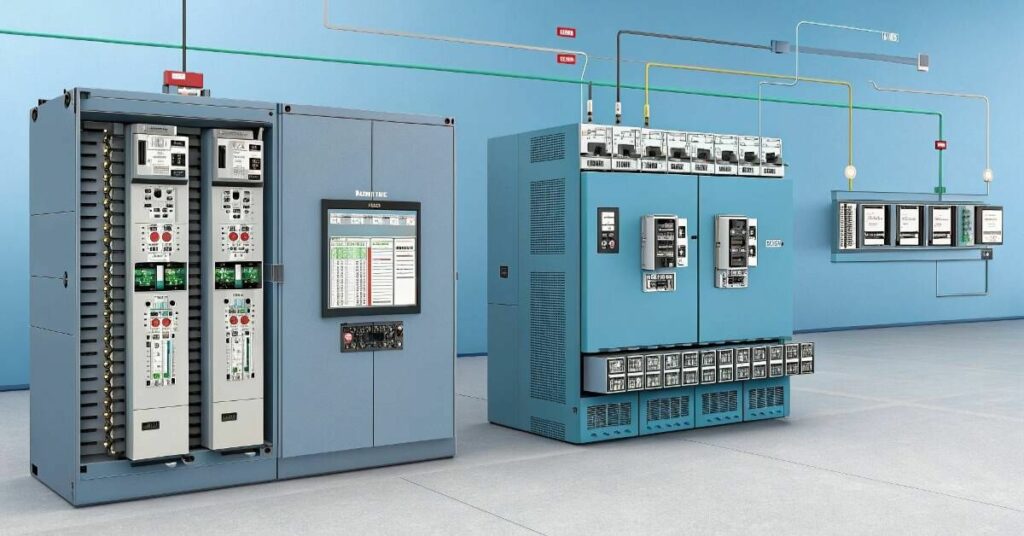

Redundancy in PLC systems is an additional system that serves as a back-up just in case the main PLC system fails. It’s as if it is a safety net for industrial automation. When one breaks, it is replaced without interruption of the process. A replica CPU, PS or Communication Link is available here. To my mind, this is the most intelligent way to secure your operations against unexpected breakdown.
High availability operations can’t afford downtime. And it takes a bit of grinding to get them all up and running, which is expensive. Redundancy ensures that things will keep running if something goes wrong. I feel it’s more than safety; it’s about being efficient and competitive. That is the reason why other industries are incorporating it as a primary part of their automation design.
Types of PLC Redundancy Architectures
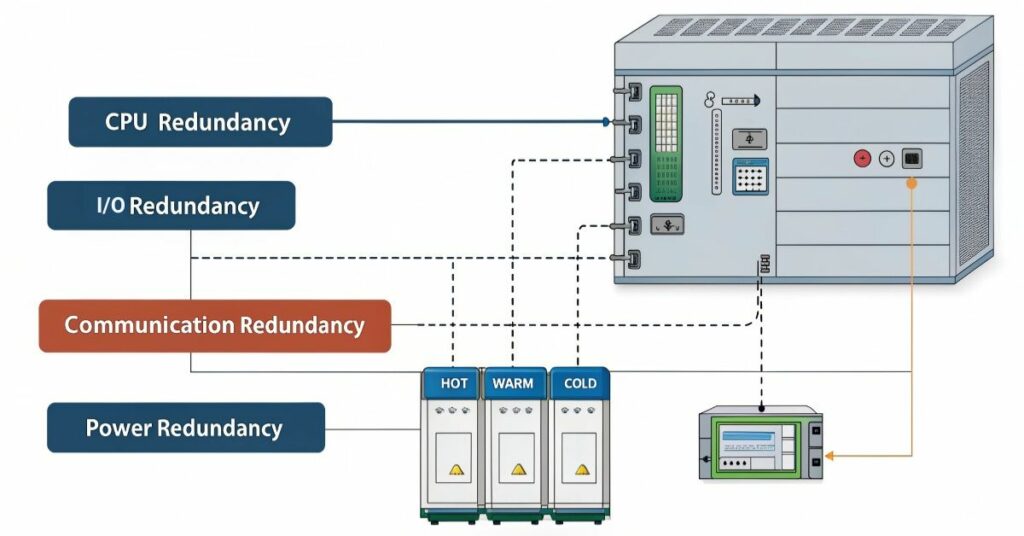
Certain redundant types of PLC systems are quite uncommon. The redundancy used in the CPU uses two processors, one active and one standby. And due to the failure of the main CPU, the backup works. I/O redundancy shields input and output modules. This then ensures the smooth operation of sensors and actuators. Communication redundancy ensures that data is still flowing even if one line within the network has fallen out. And power redundancy includes two power supplies to avoid total shutdowns. In my opinion, it’s plug and play and rock-solid reliability if you fuse them together.
Not all redundancy setups are the same. Some switch over instantly, while others take a little time.
Here’s a quick breakdown:
| Redundancy Type | Switchover Time | Backup Status | Best For |
| Hot Redundancy | Instant | Always active | Critical, nonstop processes |
| Warm Redundancy | Short delay | On standby, synced | Moderate-speed systems |
| Cold Redundancy | Longer delay | Off until needed | Budget-friendly, less critical |
Benefits of Implementing Redundancy
If one part breaks there is always a replacement. This means that there’s less downtime and more disruptions. I believe it’s a smart way to prevent expensive delays. It also enables teams to remain productive and focused even if goings on cause disruptions.
To my mind, redundancy also saves what is most valuable to you- your data and your process. It minimizes the risk of losing one’s critical information. In addition, it maintains the operational stability in case of technical faults.
Some key benefits include:
- Fewer shutdowns and system crashes
- Smooth recovery after hardware failures
- Better protection for sensitive data
- Continuous monitoring and control
Planning and Designing a Redundant PLC System
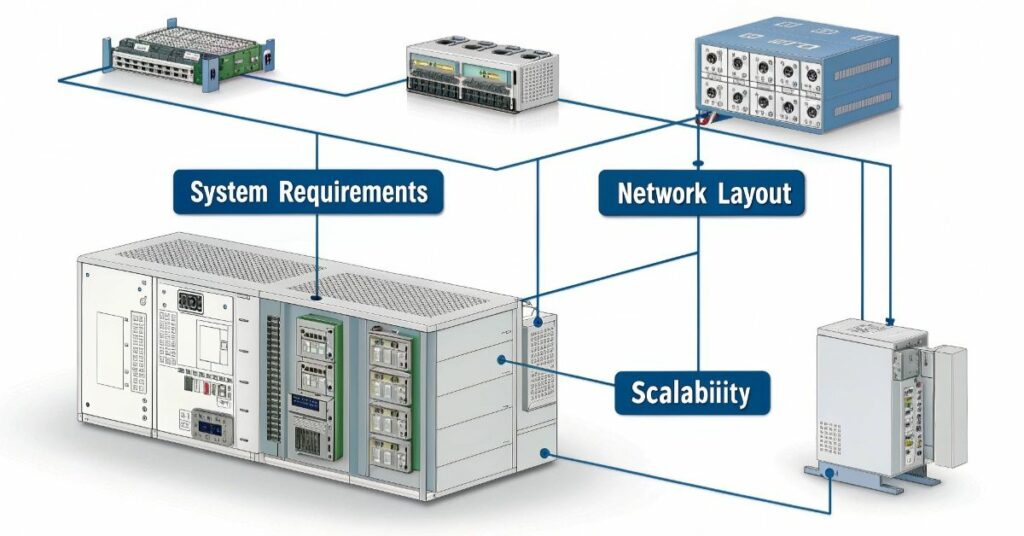
A good redundant PLC system begins with a good plan. You have to know what the PLC system is capable of dealing with. Remember current demands and future expansion. In my opinion, planning for scalability up front makes money and headaches later on.
I believe the network layout is as important as the hardware. A poor setup may confuse or slow the system down. Cables switches and connections should be placed carefully. Synchronization for correct performance guarantees that the main and backup system will operate without any lag. This leaves failovers smooth and in-detectable upon a fault.
Challenges and Solutions in Redundant PLC Deployment
Establishing a redundant PLC system is not always simple. It can be complicated quickly, particularly for large setups. With more hardware and software, of course, costs also go up. The greatest challenge that I think is facing is balancing reliability with budget. Things can spiral fast when there is no proper plan.
To my thinking, smart planning might help to overcome these problems. Standardization of the components makes it simple to control systems. Training staff decreases errors while increasing confidence. With the correct knowledge teams will be able to turn failures around quicker and maintain PLC systems better. This ensures that things flow smoothly and this is a cost saving in the long term.
Testing, Monitoring, and Maintenance of Redundant Systems
Testing is significant for redundant systems to work. Scheduled failover tests bring out the designated backups. I think it’s important to check both automatic and manual switching to avoid surprises. By doing so, you will catch problems early, before they become real problems, which saves time and money.
To my mind, continuous monitoring is the secret of long-term reliability. Monitoring PLC system performance prevents failure in the future. Preventive maintenance also makes an appearance on a large scale. With such practices your system is reliable for years.
FAQ’s
What is Redundancy in PLC Systems and why is it important?
Redundancy in PLC systems means back up hardware or communication paths that maintain continuous operation thereby minimizing downtime and system failures.
What are the types of redundancy in PLC systems?
The top types are CPU, I/O, communication and power supply redundancies which increase reliability of different sections of the system.
How do hot, warm, and cold redundancy differ?
Hot redundancy immediately follows without delay; warm has a small switchover time; whereas, cold needs manual or restart.
Conclusion
It protects from failures and reduces downtime and maintains processes at optimum. When planned and designed appropriately, redundancy has long term benefits in terms of productivity and system availability.
While redundant PLC systems have issues that make them hard to implement, the solutions are obvious. Regular (re)testing, constant surveillance, and proper maintenance are all required in order to keep everything in order. And finally, you could say that redundancy is a great investment with high availability and very few interruptions.

